Posts by Aestus
Preferential flow velocity mapping of alluvial soil using temporal electrical resistivity imaging
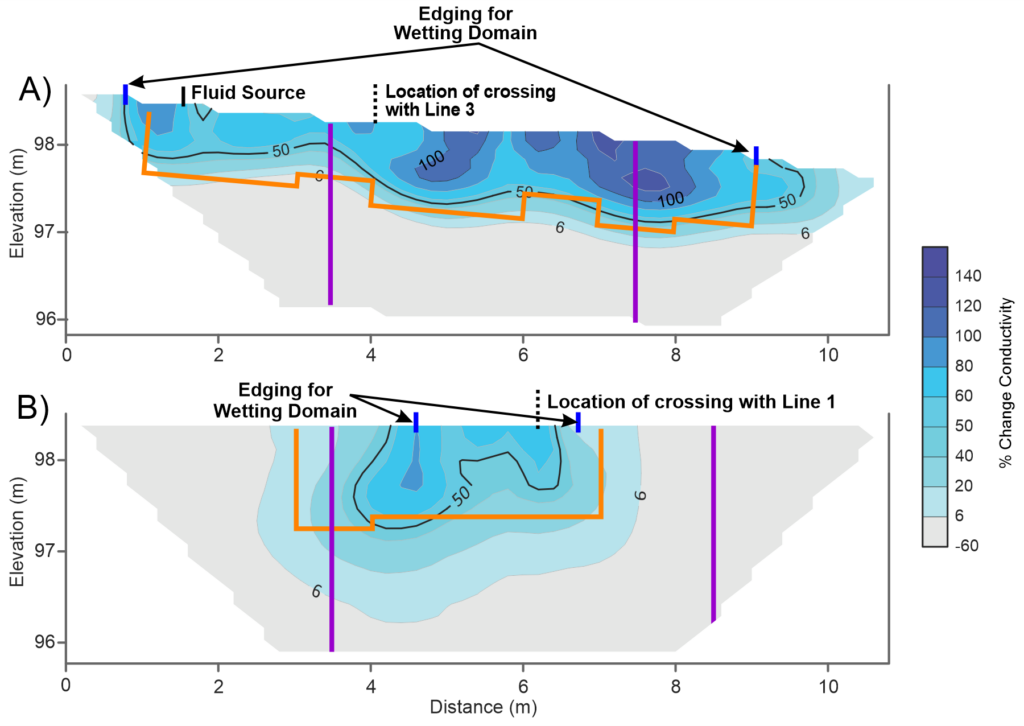
Authors: Todd Halihan, Bharat S. Acharya, John P. Hager, Lucie Guertault, Garey A. Fox Published: 10 January 2023 Abstract: Riparian soils are susceptible to the formation of macropores, which provide opportunities for preferential flow in comparison to the surrounding soil matrix. Temporal electrical resistivity imaging (TERI) can locate spatial heterogeneities in soil wetting patterns caused…
Read MoreAestus Poster “Electrical Hydrogeology Characterizes Groundwater Resources with More Certainty” at the Western Groundwater Congress
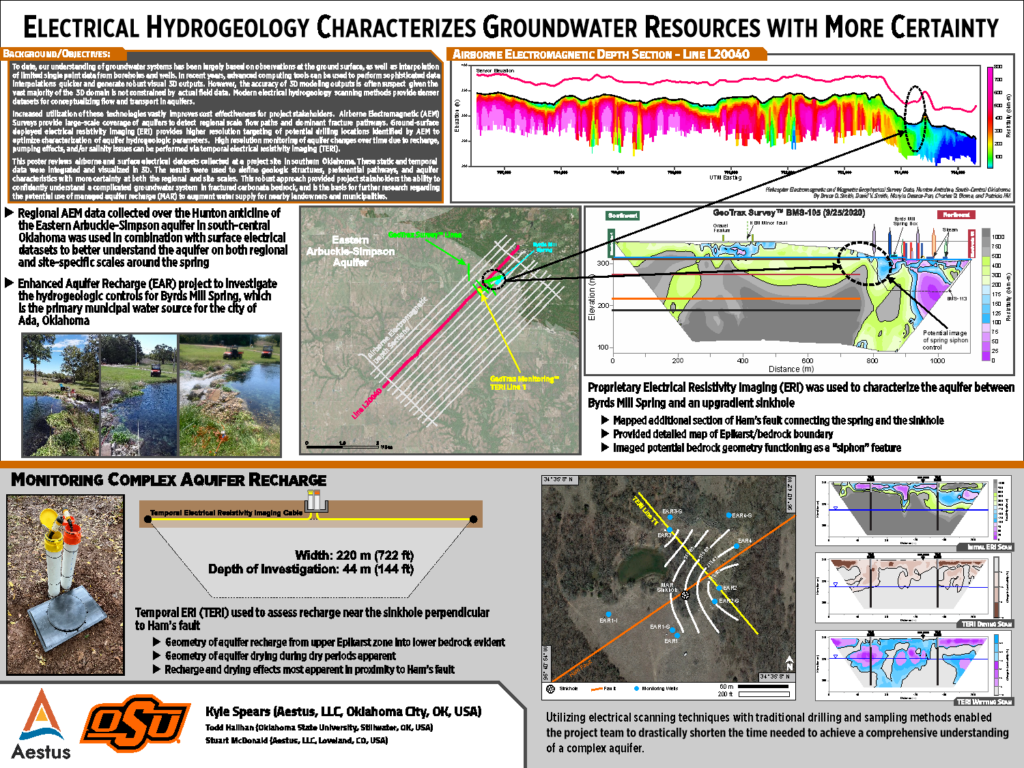
Kyle Spears, Aestus’ Technical Sales Manager/Hydrogeologist, presented a poster titled “ Electrical Hydrogeology Characterizes Groundwater Resources with More Certainty” at the Western Groundwater Congress. Abstract:To date, our understanding of groundwater systems has been largely based on observations at the ground surface, as well as interpolation of limited single point data from boreholes and wells. In…
Read MoreAestus Presents “The Next Era of Site Characterization Using Electrical Hydrogeology” at 2024 Western Groundwater Congress
Site characterization field efforts since the 1980s have demonstrated that useful conceptual site models (CSMs) typically require ultra-high data density to accurately predict subsurface contaminant distribution and groundwater transport. Some research project data showed that sites with thousands of monitoring well locations still had insufficient data density to fully characterize complex subsurface conditions, and left questions regarding conditions between the monitoring wells.
Read More